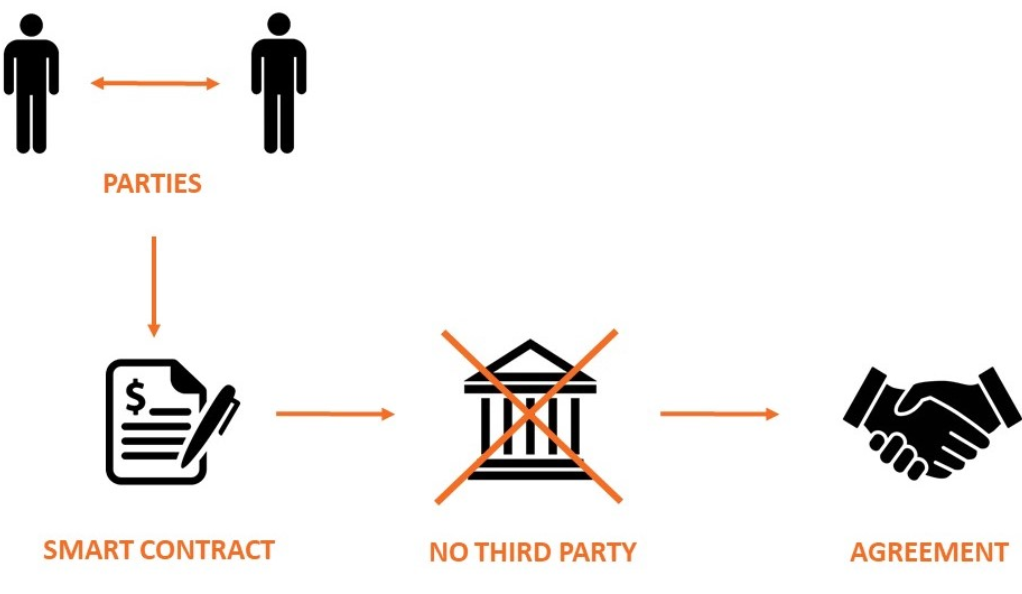
Before diving into the fascinating world of NFT transactions, it’s essential to understand the cornerstone of this digital realm—smart contracts. They are automated, self-executing contracts where the terms and conditions are stored within lines of code. This idea, although seemingly futuristic, has its roots dating back to the 1990s, long before blockchain technology became a buzzword.
As a type of digital agreement, smart contracts hold the promise of enforcing a relationship with cryptographic code. They are implemented on a decentralized blockchain network and exist as a set of promises specified in digital form. Their decentralized nature ensures that they are secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship, reducing the need for trusted intermediaries and enforcing obligations on all parties.
The Birth of Smart Contracts
The term “smart contract” was first coined by computer scientist Nick Szabo in 1994, long before Bitcoin was invented. He proposed the idea of recording contracts in the form of computer code. When predefined conditions are met, the agreements are automatically enforced.
However, it was not until the advent of blockchain technology that the concept of smart contracts began to take shape. With the rise of Ethereum, a blockchain platform that supports programmable smart contracts, this new form of digital agreement has revolutionized digital transactions. This paved the way for the advent of decentralized applications and the tokenization of digital and physical assets, thus creating the basis for NFT transactions.
The Mechanism of Smart Contracts
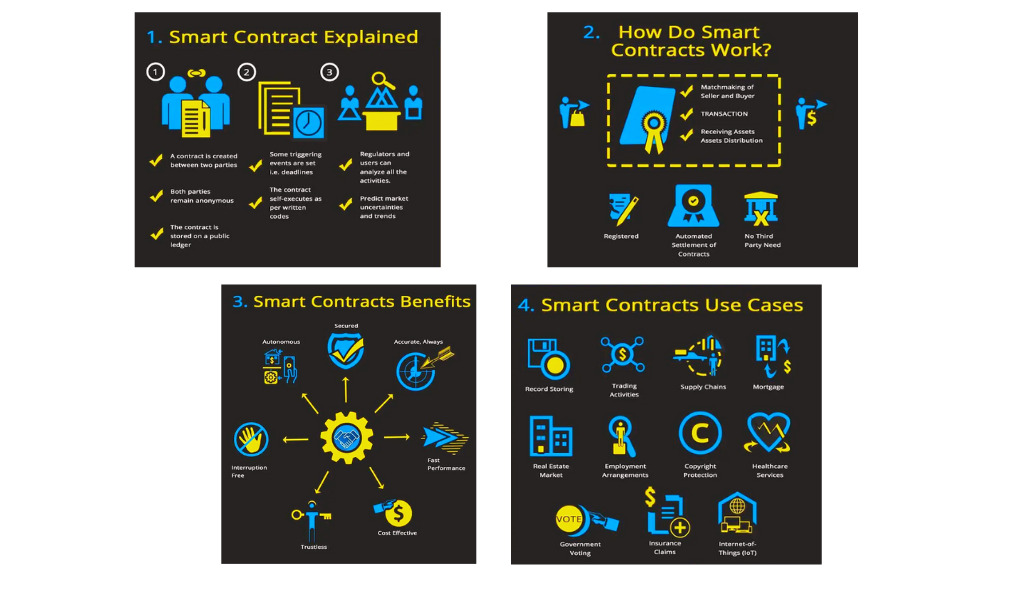
Smart contracts operate on the basic principle of “if-then” logic that is coded into a blockchain network. This mechanism involves two key factors: self-execution and security.
Self-execution
Self-execution means that once the preset conditions are met, the smart contract automatically executes itself. This eliminates the need for an intermediary, thereby reducing the risk of human error and bias. It ensures the efficient and timely execution of agreements. For example, a smart contract for a bet might automatically transfer money to the winning party when the result of a game is decided.
Security
The security of smart contracts comes from the decentralized nature of the blockchain. Transactions made through smart contracts are recorded on every computer in the network, making it nearly impossible for a single user to alter the contract. This inherent decentralization provides an impressive level of security and makes smart contracts virtually tamper-proof, which is a significant advantage in fields where trust is critical.
Understanding NFT Transactions
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork with smart contracts, it’s time to explore their role in the world of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). NFTs are digital assets that represent real-world objects like art, music, in-game items and more. They have become a popular way to buy and sell digital artwork.
How NFT Transactions Work
NFT transactions work on the principles of tokenization and uniqueness. But unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, NFTs are not interchangeable for other tokens of the same type. Each NFT contains specific information that makes it distinct from any other NFT, which gives it its value and uniqueness.
Tokenization
Tokenization is the process of converting rights to a real-world asset into a digital token on a blockchain. For example, a digital artwork can be tokenized into an NFT and sold on an NFT market. This process allows the asset to be traded on the blockchain and gives the owner the ability to prove their ownership.
Uniqueness and Ownership
Each NFT is unique, carrying specific information that distinguishes it from other tokens. This information is stored in the metadata of the token, which is immutable. Once the NFT is created, the metadata cannot be altered, ensuring that each NFT is one-of-a-kind. The blockchain also records the ownership of each NFT, establishing a clear chain of ownership. This feature allows for the provenance of assets, proving their authenticity and preventing fraud.
The remaining parts of the article would follow a similar expansion pattern, covering the remaining topics as outlined in the table.
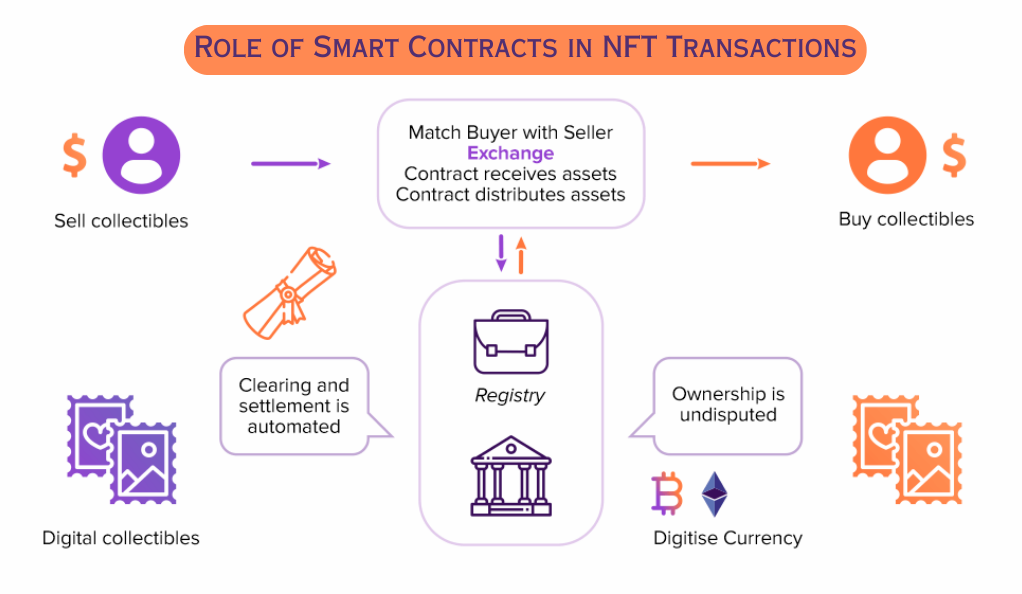
Role of Smart Contracts in NFT Transactions
Now that we’ve explained smart contracts and NFTs individually, it’s time to delve into the role of smart contracts within NFT transactions. Given their ability to enforce, verify, or facilitate the negotiation or performance of a contract, smart contracts play a pivotal role in creating, buying, and selling NFTs.
Minting and Trading of NFTs
Minting is the process of creating an NFT on the blockchain, and this is where smart contracts come into play. When an NFT is minted, a smart contract is written to the blockchain that contains the rules of the token – this includes attributes such as the token’s name, symbol, total supply, and the functions that will allow it to be traded or transferred.
When it comes to trading, smart contracts are again integral. They hold the logic for transferring tokens from one owner to another, ensuring that the transaction is securely recorded on the blockchain. This includes details such as the price of the token and the wallets of the buyer and seller.
Ensuring Authenticity and Ownership
Besides facilitating the creation and trading of NFTs, smart contracts also play a crucial role in proving authenticity and ownership of an NFT. Each NFT is tied to a smart contract on the blockchain, which contains immutable data about the token, including its original creator and ownership history.
The blockchain’s transparent nature enables anyone to verify this information. Hence, potential buyers can ascertain that the NFT was indeed created by the claimed artist and that the person selling it is the legitimate owner. This way, smart contracts help protect both creators and buyers in the NFT market.
The Future of Smart Contracts and NFTs
With NFTs exploding in popularity and smart contracts proving to be a game-changer in digital transactions, it’s worthwhile to examine the future of these two combined.
Challenges
Despite their potential, the amalgamation of smart contracts and NFTs also faces several challenges. From a legal perspective, regulatory frameworks for NFTs are still lacking. Issues such as intellectual property rights, legal recognition of digital assets, and the cross-border enforcement of smart contracts need to be addressed.
From a technical perspective, the performance and security of smart contracts are still evolving. For instance, as smart contracts are immutable once deployed, coding errors can lead to irreversible consequences. While the use of formal verification and auditing can mitigate this risk, there is no foolproof solution yet.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, the intersection of smart contracts and NFTs opens up a world of possibilities. They can disrupt various industries, from art, music, real estate, to gaming, and even finance.
For instance, in the art world, artists can tokenize their artwork into NFTs and sell them directly to collectors, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Moreover, smart contracts can be programmed to give artists a certain percentage of sales each time their artwork is resold, providing them with ongoing royalties.
Similarly, in real estate, properties can be tokenized into NFTs, allowing for fractional ownership. This could make real estate investing more accessible to average investors and simplify the buying and selling process.
Conclusion
Smart contracts and NFTs are indeed revolutionizing digital transactions. Together, they offer a secure and efficient means to create, trade, and own digital assets. While the journey ahead may pose challenges, the opportunities are truly exciting. As we continue to explore and innovate, the synergistic relationship between smart contracts and NFTs promises to reshape the digital landscape in ways we can only begin to imagine.
FAQs
1. What role do smart contracts play in NFT transactions?
Smart contracts facilitate the creation or minting of NFTs, manage their trading, and ensure the authenticity and ownership of NFTs.
2. What challenges does the combination of smart contracts and NFTs face?
Challenges include the need for a clear regulatory framework, intellectual property rights issues, cross-border enforcement of smart contracts, and potential technical glitches in smart contracts.
3. How can smart contracts and NFTs offer opportunities in various industries?
Smart contracts and NFTs can enable artists to sell their work directly and receive royalties. They can also allow for fractional ownership in real estate, making investing more accessible.
4. What are the future prospects for smart contracts and NFTs?
As sectors like art, real estate, and music increasingly embrace NFTs, the possibilities are vast. However, the journey ahead will require overcoming legal and technical challenges.
5. How does a smart contract ensure the authenticity of an NFT?
Each NFT is tied to a smart contract, which contains immutable data about the token, including its original creator and ownership history. This transparent and tamper-proof system ensures the NFT’s authenticity.