The digital revolution is undoubtedly reshaping our world in unprecedented ways. Yet, behind the exciting innovations and possibilities, there’s a darker side. Our growing digital footprint has a real-world environmental cost. Specifically, we’re going to explore the unseen environmental impacts of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and the blockchain technology that powers them.
Understanding NFTs
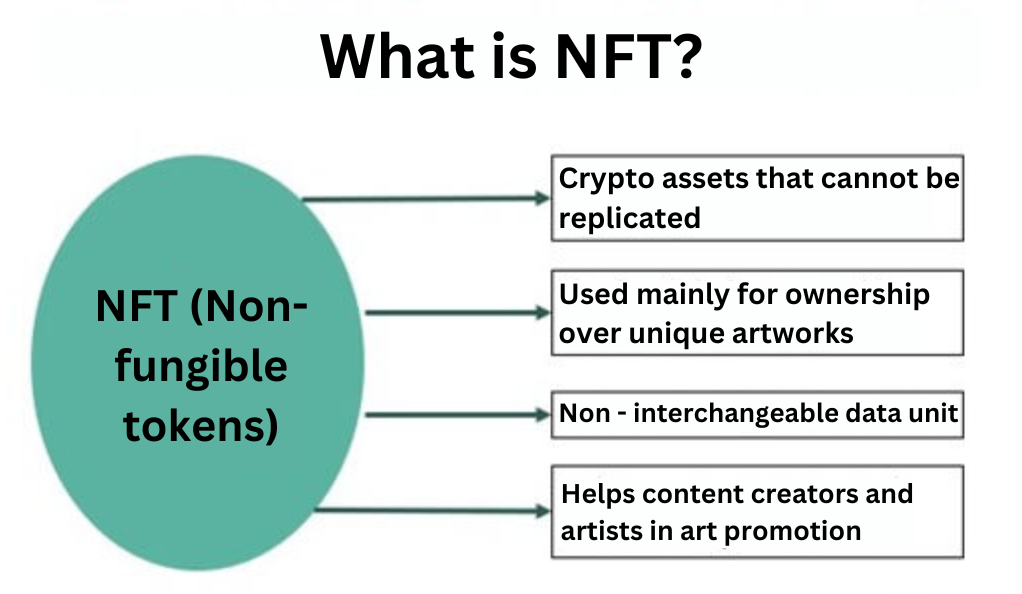
What is an NFT?
An NFT, or Non-Fungible Token, is a unique type of digital asset. Unlike other digital assets such as Bitcoin, which are fungible and can be exchanged on a like-for-like basis, NFTs are unique. They represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a unique item or piece of content. From artwork and music to virtual real estate and virtual goods in video games, the potential applications of NFTs are vast and still being explored.
How does NFT technology work?
NFTs are built on blockchain technology, the same decentralised, distributed ledger technology that powers cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. The blockchain certifies the digital asset, confirming its uniqueness and ownership. It’s like a digital certificate of authenticity that is publicly verifiable, transparent, and impossible to forge.
Blockchain and Energy Consumption
The connection between blockchain and energy
Blockchain’s energy consumption stems primarily from the proof-of-work consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. This process involves miners competing to solve complex mathematical problems, with the winner adding a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This process is highly competitive and requires massive computational power and energy.
Energy consumption in blockchain
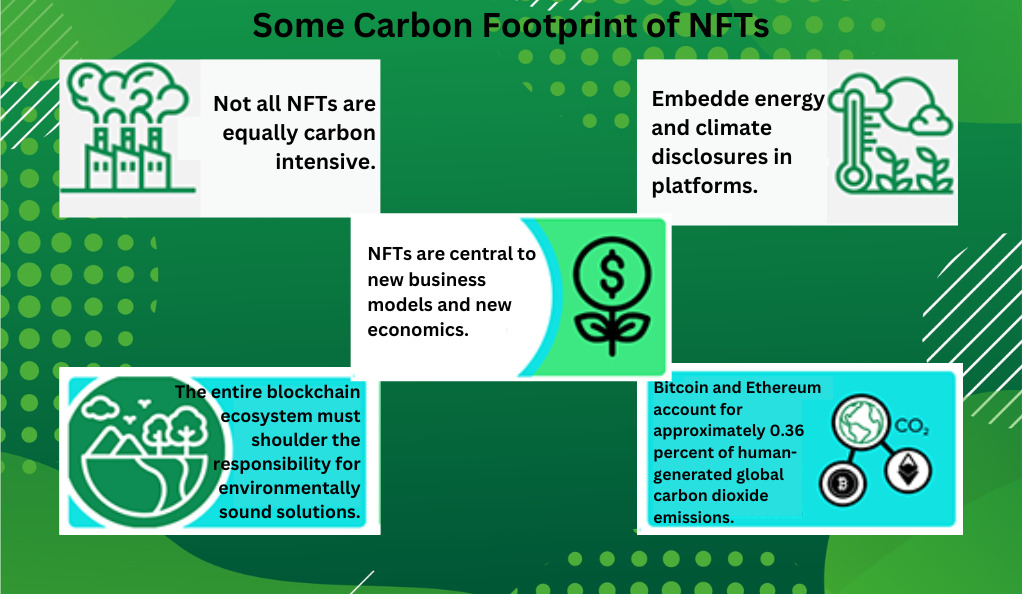
Blockchain technology’s energy consumption is enormous. Some estimates have put Bitcoin’s energy use on par with countries like Argentina. Similarly, Ethereum, which hosts the majority of NFT transactions, is estimated to use as much energy as the whole of Qatar. This high energy consumption translates into a significant carbon footprint, contributing to global warming and climate change.
NFTs and Environmental Impact
The carbon footprint of NFTs
Each NFT transaction, from minting to buying, selling, and bidding, requires energy-intensive computations, increasing the carbon footprint of NFTs. In some cases, the energy consumed for a single NFT transaction can be equivalent to an EU resident’s total electric power consumption for more than a month.
Comparing NFT energy consumption to other industries
To put things into perspective, the energy consumption of the NFT space has been likened to the energy consumption of some small nations or entire sectors like the airline industry. This startling comparison emphasises the urgency of finding sustainable solutions to reduce the energy usage in the blockchain space.
Specific Cases of NFT Energy Consumption
Art and NFTs
The advent of NFTs has dramatically revolutionised the art world by offering artists a new platform to monetise their work. However, the environmental cost of minting artworks as NFTs is profound. Some artists are becoming more aware of this and are seeking greener alternatives or offsetting the carbon emissions of their NFT sales.
Gaming and NFTs
The intersection of NFTs and gaming is a growing trend, with players now able to own unique in-game items as NFTs. While this opens up exciting new possibilities for the gaming industry, it also amplifies the energy consumption and environmental impact of the NFT space.
Possible Solutions and Sustainable Alternatives
Energy-efficient blockchain technologies
One potential solution to the energy problem is to transition to more energy-efficient blockchain technologies. Ethereum, for instance, is planning to switch to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which is expected to significantly reduce its energy consumption.
Greener NFT platforms
Some NFT platforms are taking steps towards sustainability. These platforms are either moving to more energy-efficient blockchains, offsetting their carbon emissions, or both. However, there’s still a long way to go before these practices become the norm in the industry.
Role of Individual Responsibility
NFT artists and environmental responsibility
Artists who choose to mint their work as NFTs need to understand the environmental impact of their actions. This understanding may encourage them to seek greener alternatives or offset the carbon emissions generated from their NFT transactions.
NFT collectors and environmental responsibility
As consumers, NFT collectors also have a role to play. By prioritising greener platforms and artists who are mindful of their carbon footprint, collectors can help drive the demand for more sustainable practices in the NFT space.
The Future of NFTs and the Environment
Looking ahead, we need to strike a balance between the benefits of NFTs and their environmental impact. The adoption of sustainable practices needs to be at the forefront of blockchain technology development and the operation of NFT marketplaces. As the NFT space continues to evolve, so too should our approach to mitigating its environmental impact.
Conclusion
While the advent of NFTs has brought about new opportunities and transformed the digital asset landscape, we cannot turn a blind eye to their environmental impact. From the artists who mint NFTs to the collectors who buy them, every participant in the NFT ecosystem has a role to play in driving the industry towards a more sustainable future.
FAQs
1. What is an NFT?
An NFT is a non-fungible token, a type of digital asset that represents a unique item or piece of content.
2. Why do NFTs have a high energy consumption?
NFTs use blockchain technology, specifically proof-of-work blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which require significant computational power and energy.
3. What are some potential solutions to the environmental impact of NFTs?
Possible solutions include using more energy-efficient blockchain technologies, greener NFT platforms, and the responsible behavior of artists and collectors.
4. What is the role of individual responsibility in mitigating the environmental impact of NFTs?
Both NFT artists and collectors have a responsibility to understand the environmental impact of their actions and drive the shift towards more sustainable practices.
5. Can the environmental impact of NFTs be offset?
Yes, some NFT platforms and artists offset the carbon emissions of their NFT transactions, but this practice needs to be more widely adopted.